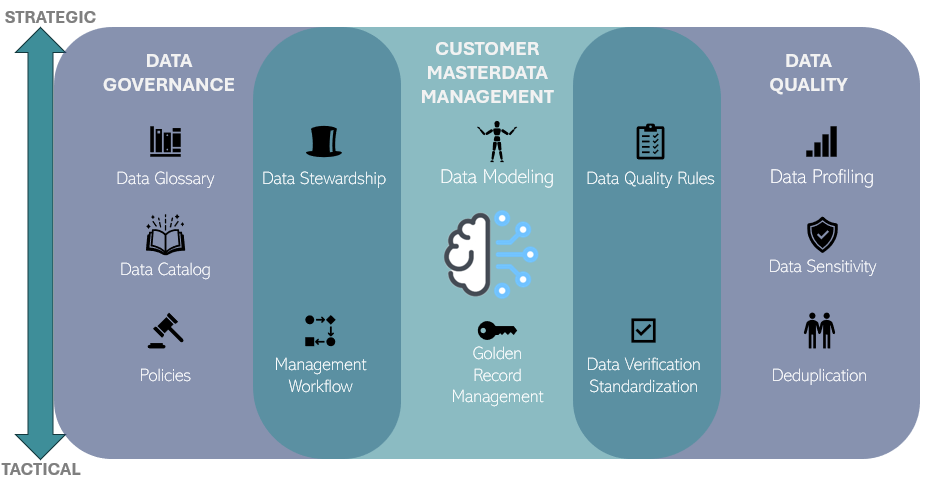
Customer master data management (CMDM) is essential for any business aiming to build a reliable, unified view of its customers. Without well-managed customer data, organizations risk inefficiencies, poor customer experiences, and misguided decisions.
Drawing on proven best practices, including those embraced by Pretectum CMDM, we’ve outlined ten practical steps to elevate your customer master data management and unlock its full potential.
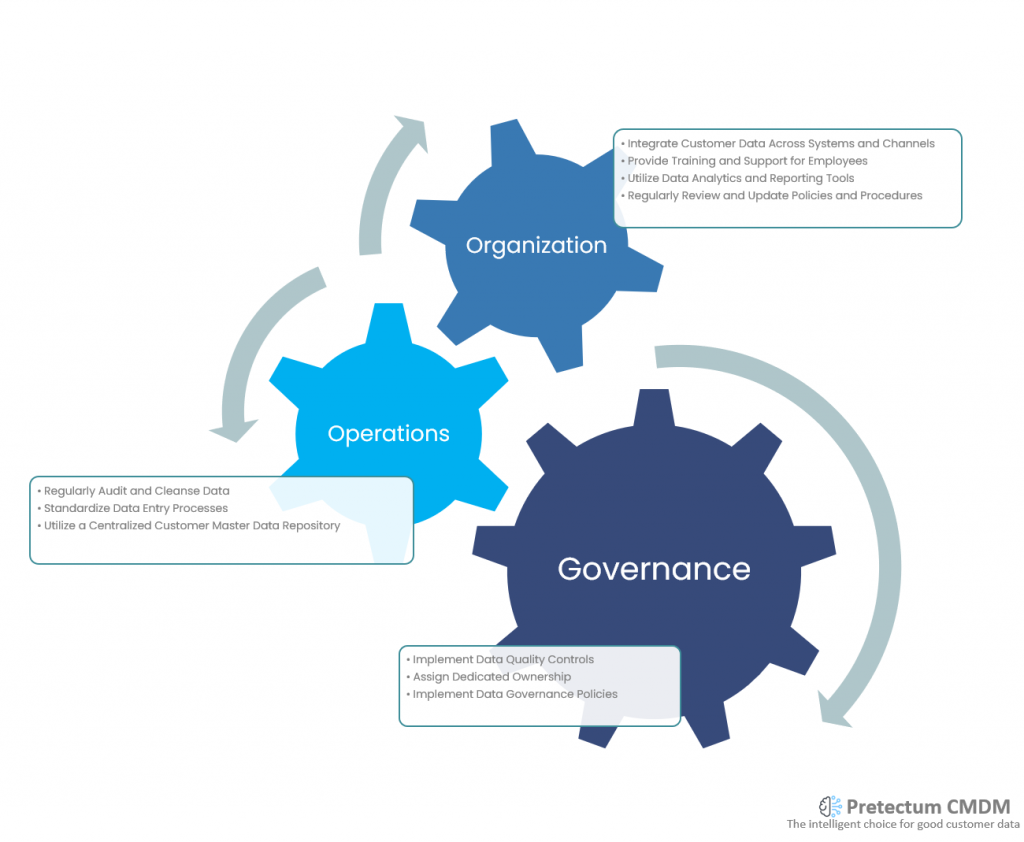
1. Implement Data Quality Controls
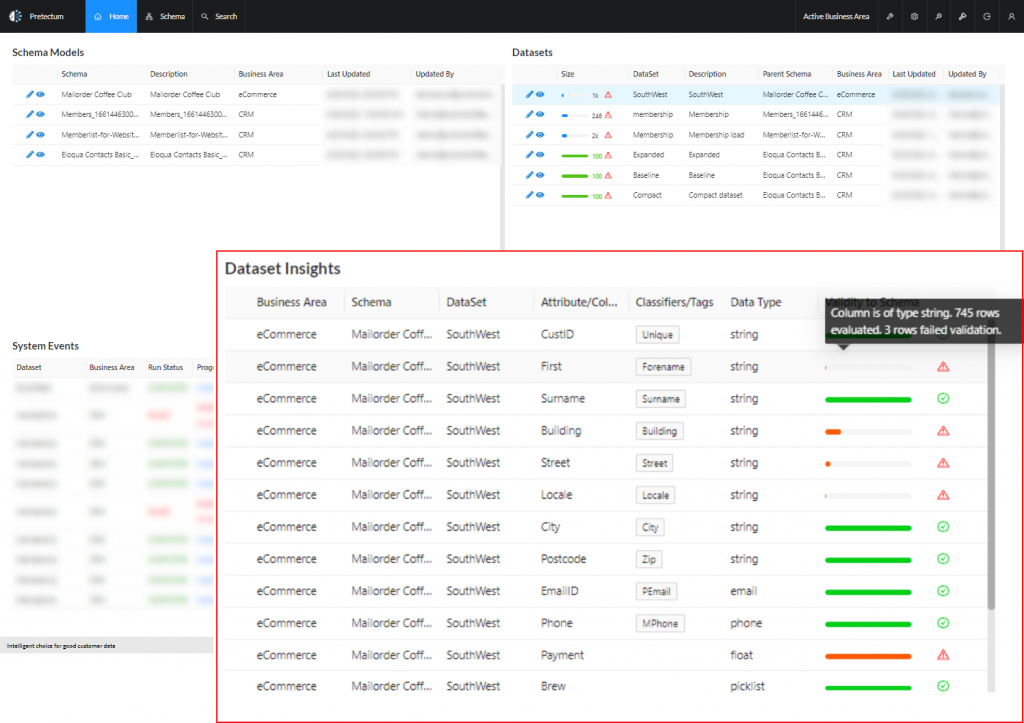
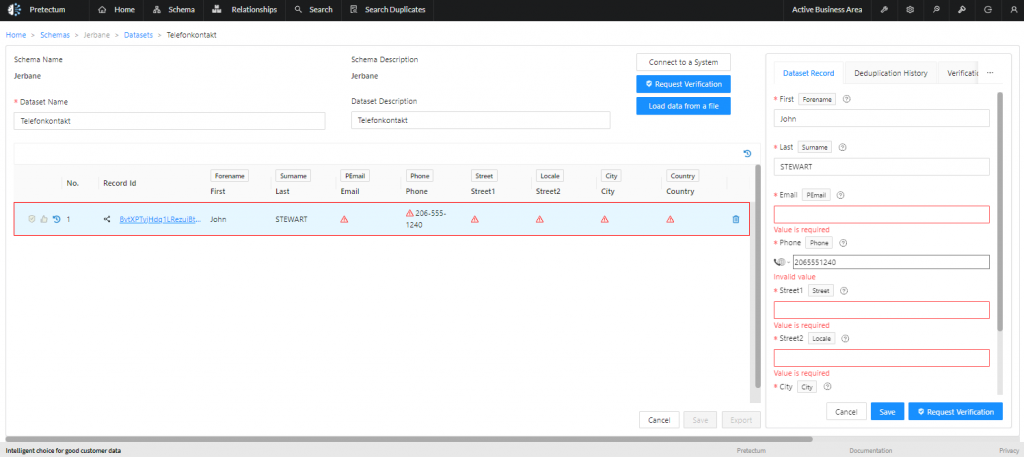
Accurate, up-to-date customer information is the foundation of effective Customer MDM (CMDM). Establishing data quality controls early on at the point of entry and throughout the data lifecycle helps prevent errors from creeping in. This includes mandatory field validations, format checks, and automated verification against trusted reference data. By catching issues early, you reduce costly clean-up later and ensure your customer data remains trustworthy for all users.
2. Assign Dedicated Ownership
CMDM thrives when a dedicated team or individual takes responsibility for overseeing customer master data. Such a role assignment involves monitoring data quality, coordinating updates, and enforcing governance policies. Having clear ownership creates accountability and ensures data management is not an afterthought but a continuous priority aligned with business goals.
3. Regularly Audit and Cleanse Data
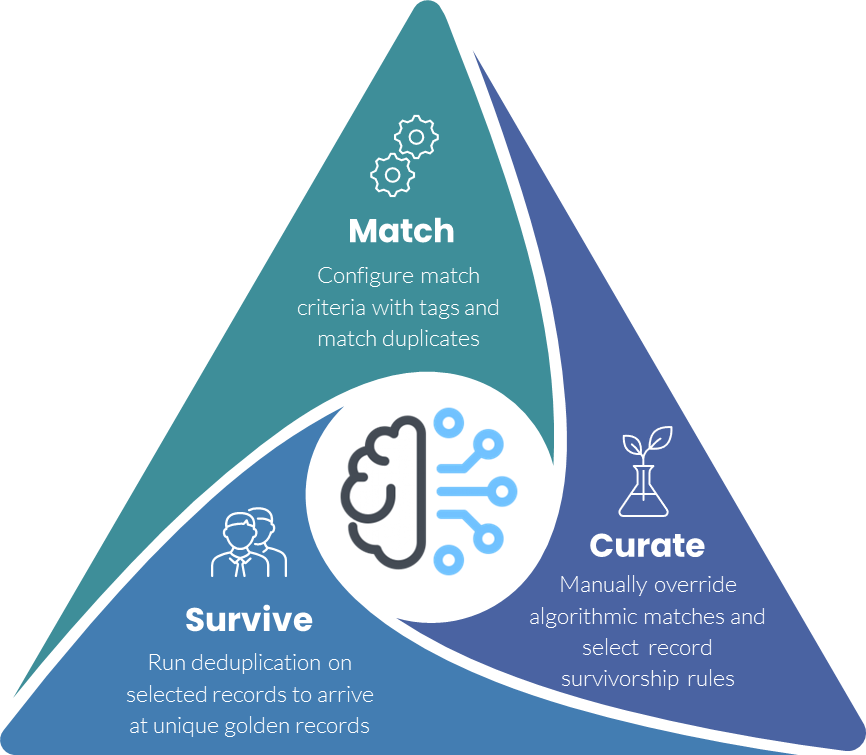
Even with controls, customer master data can become outdated or duplicated over time. Regular audits and cleansing routines are critical to identify and remove duplicates, correct inaccuracies, and archive obsolete records. Scheduled data maintenance-quarterly or biannually-helps maintain a clean, reliable customer master dataset that supports accurate analytics and personalized engagement.
4. Standardize Data Entry Processes
Consistency is key in CMDM. Standardizing how customer data is entered-such as using uniform formats for names, addresses, and contact details-reduces variation and errors. Developing a comprehensive data dictionary and providing clear guidelines for data entry ensures that all teams capture information in a consistent manner, simplifying integration and reporting.
5. Implement Data Governance Policies
Effective CMDM requires formal data governance that defines roles, responsibilities, and access controls. Governance policies specify who can create, update, or delete customer data, how data quality is monitored, and how compliance with privacy regulations is maintained. This framework safeguards data integrity and security while enabling controlled collaboration across departments.
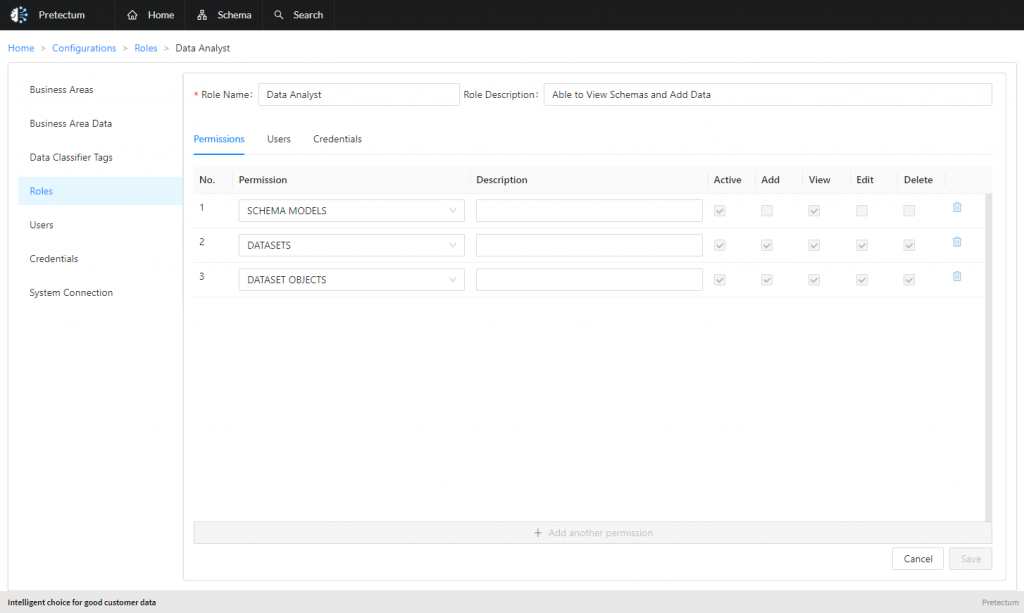
6. Utilize a Centralized Customer Master Data Repository
Centralizing customer data into a single repository is a cornerstone of CMDM. A unified system of record eliminates silos and ensures all stakeholders access the same accurate data. Pretectum CMDM’s platform excels here by providing a scalable, secure centralized repository that integrates seamlessly with existing systems, making data management more efficient and reliable.
7. Integrate Customer Data Across Systems and Channels
Customers interact with businesses through multiple touchpoints-sales, support, marketing, and more. Integrating customer data across all systems and channels creates a holistic, 360-degree view of each customer. This unified perspective enables personalized experiences and informed decision-making, reducing friction caused by inconsistent or fragmented data.
8. Provide Training and Support for Employees
Human error is a major source of data quality issues. Providing regular training and clear documentation on proper data management practices empowers employees to enter and maintain customer data accurately. Ongoing support helps reinforce standards and fosters a culture that values data quality as everyone’s responsibility.
9. Regularly Review and Update Policies and Procedures
Business needs and regulatory landscapes evolve, so CMDM policies and procedures should be reviewed and updated regularly. This ensures your data management practices remain aligned with current compliance requirements and operational priorities. Continuous improvement keeps your CMDM program agile and effective over time.
10. Utilize Data Analytics and Reporting Tools
Finally, leveraging data analytics and reporting tools unlocks insights from your customer master data. Analyzing customer behavior, preferences, and trends helps tailor marketing, sales, and service strategies. Pretectum CMDM’s support for advanced analytics capabilities enable organizations to transform raw data into actionable intelligence, driving better customer engagement and business outcomes.
To learn more about how Pretectum CMDM addresses each of these contact us today.


