Organizations can leverage customer data for competitive advantage by creating personalized experiences and tailoring offerings and communications to individual preferences, which increases customer engagement and loyalty.
Sounds simple enough, right?
Effective data management allows businesses to respond swiftly to market changes, adapt strategies based on customer insights, and introduce innovative products or services that align with customer needs; however, all of those ideas and initiatives need accurate customer data. Quality in the customer data is crucial for meaningful analysis and decision-making, whilst proper data management processes improve data quality and resource allocation. So how might you go about getting more advantage? Here are a few ideas for you to mull over.
Building a Custom Customer Data Platform (CDP): Instead of buying a pre-built CDP, CRM, DMP or CMDM solution, organizations can explore the option of building a custom customer data platform, one that allows them to tailor the platform to their specific needs and gain a competitive edge through unique data management capabilities.
The idea of building a Custom Customer Data Platform (CDP) stems from the need for organizations to have a more personalized and effective way of managing their customer data. Such a system aggregates and organizes customer data across a variety of touchpoints and is used by other software, systems, and marketing efforts; collecting and structuring real-time data into individual, centralized customer profiles.
This would allow for a unique, unified view into customers’ minds and needs. The concept of a custom CDP comes into play when organizations want to tailor the platform to their specific needs and gain a competitive edge through unique data management capabilities. This would involve selecting best-in-class componentry for each layer of the customer data journey.
Building a custom CDP is not a simple task though. To engage in such an undertaking requires It requires clarity on design, the right resources, a deep enough budget, and a considerable amount of time. The benefits of having a custom CDP that aligns perfectly with an organization’s needs might meet or fail to meet expectations.
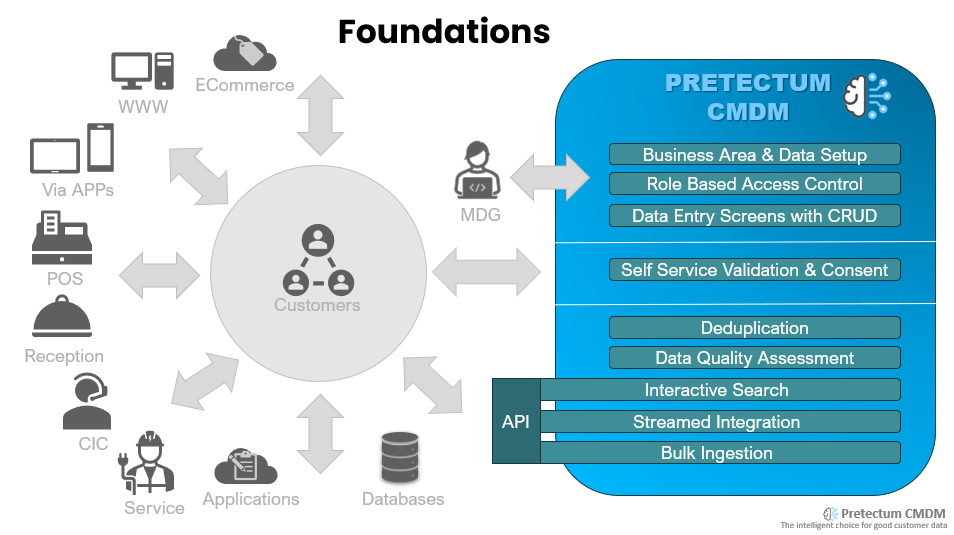
Implementing Privileged Insights: The concept of “Implementing Privileged Insights” comes from a Harvard Business Review article written by Ian Kahn, Paul Leinwand, and Mahadeva Matt Mani.
The authors suggest that companies can gain a competitive advantage by creating and integrating unique and relevant information about customers into their decision-making processes. This way, companies can gain a competitive advantage by creating and integrating unique and relevant information about customers into their decision-making processes, which competitors do not have access to.
This can be achieved by observing and interacting with customers while they use products and embedding privileged insights into existing customer touchpoints. That’s fine if you’re running a webshop, have a mobile app or have the ability to serve up those privileged insights. You’ll still potentially have a data quality problem and you’re still building a custom CDP.
Radically Different Approach to Digital Experience (DX): Organizations can take a new approach to digital transformation by focusing on organizational buy-in, metrics that matter, categorizing the customer, democratizing the data, and leveraging the SEO benefits of personalization. This idea is a synthesis of several concepts in the field of digital transformation and customer experience management.
Composable DX: This concept emphasizes a modular and flexible approach to delivering digital experiences as suggested by CEO and co-founder of Pimcore Dietmar Rietsch. This allows organizations to create custom digital experiences that align with their unique business needs and customer expectations. Such an approach requires organizations to prioritize agility, flexibility, adaptability, effective communication, composable thinking, and empathy toward customers.
Digital Transformation (DX): uses digital technologies to create new or modify existing business processes, culture, and customer experiences to meet changing business and market requirements. The need for digital transformation has been highlighted by the disruption caused by events like the COVID-19 pandemic.
Customer Experience Management: This involves providing a seamless user experience, fixing any issues quickly, and understanding and adapting to user behaviors.
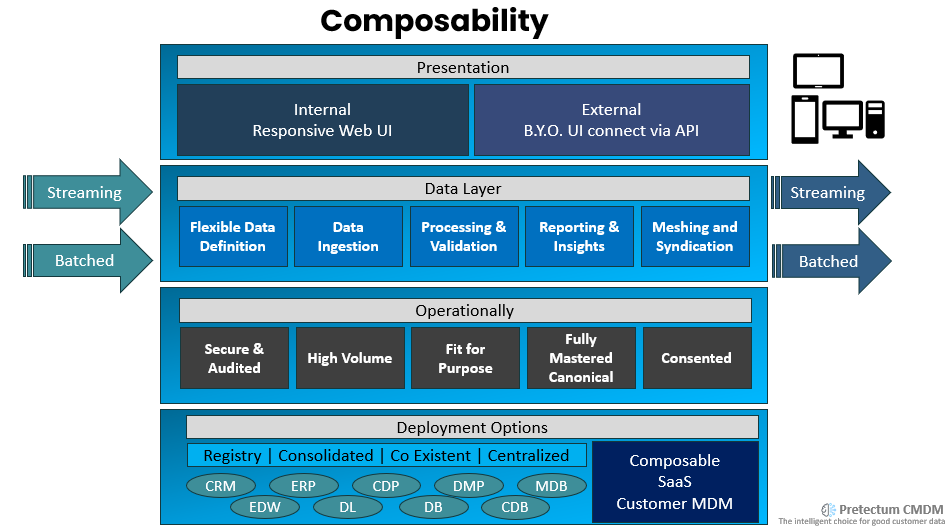
In the end, it isn’t about technology or radical ways of doing different things beyond making better use of customer data; most of the time it is about having a better understanding of customer behaviour and preferences, by analyzing customer data. That’s assuming you have the data and it is of good enough quality.
You can gain insights into customer behaviour and preferences with almost any customer data repository but if you want it to help you tailor your products, services, and marketing efforts to meet the specific needs and wants of your customers you need to ensure that the data is broad enough, deep enough and of sufficient grade to meet to analytics needs.
Customer data can also be used to identify inefficiencies in your operations and improve processes. This can lead to cost savings and improved customer satisfaction. Again, the dependency here is the breadth and quality of the data.
By gathering your data on individual customers into unique profiles and storing them in a single location like the Pretectum CMDM, you can match customer interactions with the right contact profile. This in its turn allows you to deliver personalized marketing messages that pique your customer’s true interest.
Superior data analysis can confer a competitive advantage. However, it’s important to note that the data must offer high and lasting value, be proprietary, lead to improvements that can’t be easily imitated, or generate insights that can be quickly incorporated
By embedding a data-led approach in all customer-focused efforts and goals, organizations can achieve customer-centricity by maintaining clarity on customer value, understanding the customer journey, and fostering exceptional customer experiences at every stage. This radically different approach relies heavily on data as a solid foundation for customer success. A CMDM is perfectly positioned to support such an approach.
Organizations can balance the need for data collection with customer privacy concerns by implementing the following strategies:
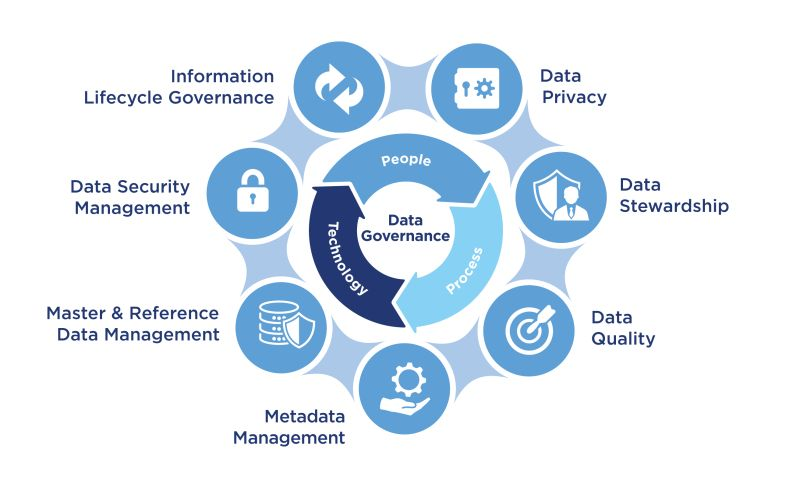
Gather Only the Essentials: Collect data that is essential for business purposes and inform customers about how it will be used. This in its turn promotes transparency and helps in building a mutually beneficial relationship.
Obtain Consent for Sensitive Information: When obtaining sensitive information from customers, seek their permission before using it. If a customer refuses to provide consent, refrain from using the data.
Data Analysis and Customer Consent: Utilize data analysis to understand customer behaviour and preferences. Additionally, communicate with customers about the intended use of their information, ensuring that their consent is obtained before proceeding.
Understand the Value and Risks of Data: Organizations should comprehensively understand the value and risks associated with the data they collect. This understanding will help in prioritizing data collection and drawing additional insights from the available data.
Establish Clear and Transparent Communication: Communicate clearly with customers, employees, and partners about the collection, storage, and use of data. Respect their preferences and consent, and collaborate with other businesses, organizations, and authorities to share best practices and insights.
Design for Transparency and Trust: You should design products and services with transparency and data privacy in mind. You must provide customers with appropriate value in exchange for data, educate them about how it is collected, and allow them to have control over it.
Not prioritizing customer privacy when collecting data can lead to several potential consequences.
Non-compliance with data privacy regulations can result in severe penalties, including hefty fines. Prioritizing data privacy ensures that businesses adhere to the necessary legal requirements. Failure to comply with data privacy regulations could result in steep fines, potentially costing a company a significant amount relative to sales turnover.
Data breaches and privacy violations can shatter customer trust in an instant. High-profile data breaches have made headlines, exposing the personal information of millions of individuals. Prioritizing data privacy is essential for safeguarding customer trust and maintaining a positive brand reputation.
Not prioritizing customer privacy can lead to financial and reputational risks for businesses. Data breaches and privacy violations can have a significant impact on a company’s financial standing and reputation.
If you recognise data as a valuable asset, you then prioritize data privacy and gain a competitive edge. Failing to prioritize customer privacy can lead to a competitive disadvantage. Failure to prioritize data privacy can result in a loss of customer confidence, leading to weaker relationships and reduced customer loyalty.
Organizations can gain a competitive advantage by leveraging customer data for personalized experiences. Effective data management allows businesses to respond to market changes, adapt strategies, and introduce innovative products.
Building a custom Customer Data Platform (CDP), implementing privileged insights, and adopting a radically different approach to Digital Experience (DX) are ways to enhance data management. Balancing data collection with customer privacy is crucial, involving strategies like gathering only essential data, obtaining consent, and designing for transparency. Failure to prioritize customer privacy may result in legal consequences, loss of trust, and financial risks.
Recognizing data as valuable and prioritizing privacy is key for sustained success and customer loyalty.




