“Thick data” refers to qualitative information that provides insights into the context, emotions, and human experiences associated with a particular phenomenon.
Thick Data is often contrasted with “big data,” which typically consists of large volumes of quantitative and structured data. While big data is valuable for statistical analysis and identifying patterns, thick data adds depth and richness by offering a more nuanced understanding of the social and cultural factors influencing a situation.
Thick data is usually collected through methods such as interviews, ethnographic studies, participant observations, and open-ended surveys. These approaches allow researchers to gather subjective and context-specific information that may be challenging to capture through quantitative means alone. The combination of big data and thick data is often seen as a holistic approach to gaining comprehensive insights into complex phenomena.
“Thin data” is a term that might be used to describe a small amount of information or data points that may lack depth or context. Unlike big data, which involves massive datasets with diverse and complex information, thin data typically refers to limited and less detailed datasets. This Thin Data may not provide a comprehensive understanding of a particular subject, and its analysis may be more straightforward compared to the intricate analysis required for big data.
In some cases, the distinction between thick data and thin data is made to highlight the depth of qualitative insights (thick data) versus the limited and often quantitative nature of some datasets (thin data). The Thin Data might be more readily available but may not capture the full complexity or richness of a situation. It’s essential to consider the quality, relevance, and depth of data when making decisions or drawing conclusions based on thin data.
It’s easy to say an organization should make customers their north star. Yet the reality is many organizations remain product and service-focused and are far from customer-centric. To tackle the challenge of customer-centricity and improve the overall customer experience, businesses need to execute a strategy that is business culture-aligned and technologically provides an advantage.
The concept of Thick Data gained prominence through a 2016 TEDx Cambridge talk and a compelling Ethnography Matters article by former Nokia researcher Tricia Wang. Thick Data is a derivative of qualitative methods, it offers insights into the emotional and motivational aspects of people, shedding light on their thought processes. This goes beyond mere facts and behaviors, providing crucial context and narrating the stories that “breathe life” into the numbers and statistics associated with the customer.
Big Data emphasizes quantification and numerical analysis, Thick Data reminds us of the human side of business, capturing the nuances that might be overlooked in the proverbial sea of spreadsheets and graphs.
The Duality of Big Data and Thick Data
Big Data and Thick Data, though seemingly at odds, play complementary roles in driving optimal business decisions. Big Data analytics focuses on incremental improvements, optimizing existing systems based on data-generated insights. In contrast, Thick Data analytics ventures into the realm of change, challenging the status quo and uncovering transformative opportunities, albeit on a smaller scale.
The sweet spot lies in integrating both types of data, especially in understanding the customer experience. Big Data reveals what customers are doing and where improvements can be made, while Thick Data uncovers the reasons behind their behaviors and their desires for a different experience.
Customer Master Data Management: A Holistic Approach
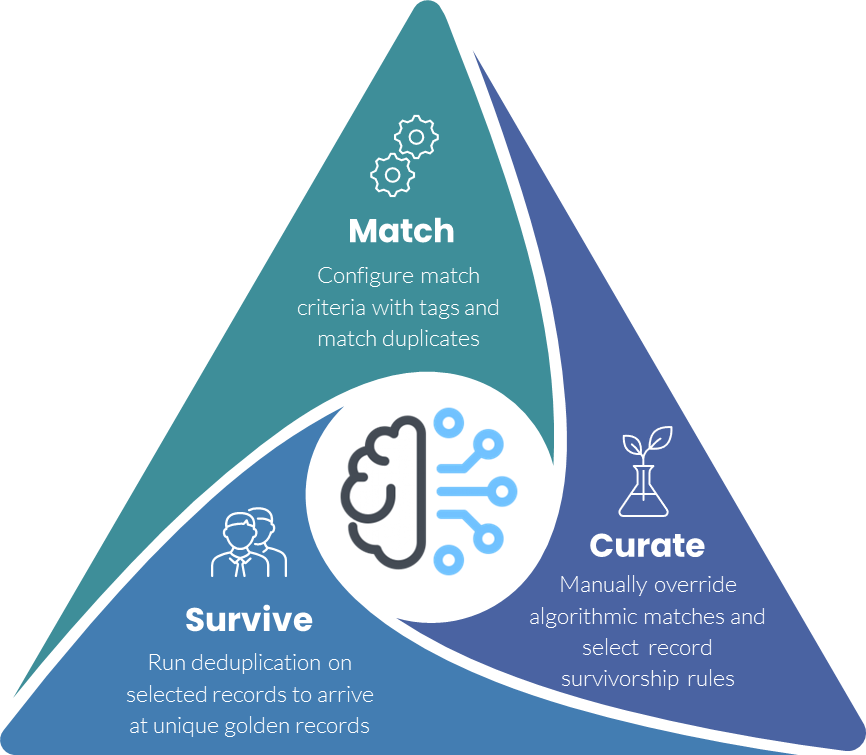
With Customer Master Data Management (CMDM), the integration of Big Data and Thick Data can be pivotal. CMDM involves the meticulous process of gathering, curating, analyzing, and syndicating customer data.
The Thick
Thick Data in CMDM can originate from qualitative sources such as customer interviews, feedback sessions, and ethnographic studies, such methods delve into the emotional and motivational aspects of customers, with a deeper understanding of customer preferences, experiences, and expectations. Qualitative insights, for example, might reveal that a customer’s loyalty is tied to personalized interactions rather than just transactional efficiency.
Thick Data in CMDM can be profoundly impactful as it adds a layer of context to the quantitative metrics gathered through CMDM processes, enabling organizations to tailor their strategies to align with the genuine needs and desires of their customers. When CMDM decisions are informed by Thick Data, they are rooted in statistical analysis and reflect a deep understanding of the humanness behind customer records.
The Thin
Thin Data in CMDM more typically comes from quantitative sources such as transactional records, purchase history, and demographic data – effectively your transactional systems like POS, CRM, ERP, or even CDP. Thin Data lacks the depth of qualitative insights but provides essential information for CMDM processes. Pattern analysis in Thin Data might reveal the most popular products among a certain demographic or suggest the frequency of customer interactions.
Thin Data is valuable in CMDM for its efficiency in handling large volumes of information because you provide it in aggregate, not in detail! This Thin Data forms the backbone of the structured datasets in support of the customer record, allowing you to identify potential trends, patterns, and correlations that can contribute to better-informed decision-making.
Relying solely on Thin Data without the enriching context of Thick Data might lead to overlooking the intricacies of customer behavior and preferences.
For leaders steering various Customer Master Data Management initiatives, embracing both Thick and Thin Data is important. The integration of these data allows for a comprehensive understanding of customer behaviors, preferences, and expectations. Creating a customer-centered A.U.R.A.
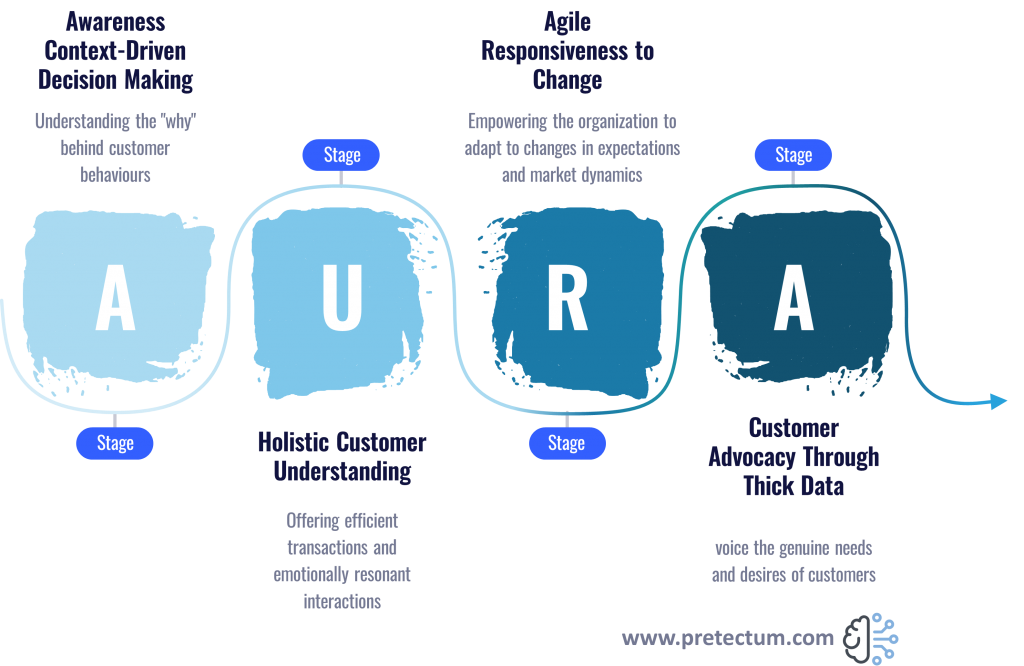
Awareness through Context-Driven Decision Making
Data management leaders who focus on customer analytics should champion a culture where business decisions are not solely based on quantitative metrics but are also influenced by the qualitative context provided by Thick Data thereby understanding the “why” behind customer behaviors. This enables more context-driven decision-making through CMDM.
A Holistic Customer Understanding
CMDM processes that incorporate both Thick and Thin Data ensure a more holistic understanding of customers. This holistic single-customer view enables organizations to tailor their approaches, offering not just efficient transactions but emotionally resonant interactions that build lasting customer relationships.
Facilitating Agility in Response to Change
While Thin Data facilitates agile responses to incremental improvements, Thick Data equips analytical leaders to identify and respond to transformative opportunities. A balance between these data types empowers organizations to adapt to changing customer expectations and market dynamics.
Advocacy for the Customer through Thick Data
Being able to advocate for customers, customer data management leaders can play a pivotal role in CMDM. Thick Data becomes the vehicle to facilitate additional tooling for customer advocacy, allowing leaders to voice the genuine needs and desires of customers, challenging the status quo, and driving meaningful change.
Consider next, the very real impact that the insights from your CMDM might have on your data systems landscape in terms of practices and technologies. These might include all or just some of the following :
Leverage curated customer data to build robust personalization engines, that utilize customer preferences, purchase history, and behavior data to tailor marketing messages, product recommendations, and website content to individual customers. Personalization enhances the overall customer experience by making interactions more relevant and engaging.
The use of historical customer data in predictive analytics can forecast customer behaviors, such as purchasing patterns or potential churn. By understanding these trends, businesses can proactively address customer needs, offer personalized incentives, and prevent issues before they arise.
Consolidated customer data gives a comprehensive view through the integrated data from various touchpoints (sales, marketing, support) into the CMDM to create a holistic customer profile. This 360-degree view ensures that every interaction is informed by a complete understanding of the customer, leading to more meaningful engagements.
The use of customer data to enhance automated support systems.supports AI-driven chatbots or virtual assistants that leverage customer records to provide personalized support. These systems can understand customer history, preferences, and past interactions, delivering efficient and tailored assistance.
Curated customer feedback that gets analyzed can provide insights into customer sentiment along with text mining techniques to extract valuable insights from customer reviews, surveys, and feedback. This information can guide product improvements, service enhancements, and overall business strategy. But you need to bring it all to a relationship with a master, best served by CMDM.
You might want to anticipate and address customer issues before they escalate. If you leverage historical customer data you might be able to identify patterns that precede common issues. Implement proactive measures, such as targeted communication or personalized offers, to prevent problems and enhance the customer experience.
Customer segmentation based on curated data and demographics, behavior, or preferences is almost a “table stakes” use case, with which you can tailor marketing campaigns for each segment, ensuring that promotions and messaging resonate with specific customer groups.
Keeping track of an understanding of the customer journey for strategic marketing by way of a map of the customer journey using data on touchpoints, interactions, and behaviors. can be useful in developing targeted marketing strategies aligned with different stages of the customer lifecycle, fostering long-term relationships.
The use of customer behavior data is especially useful for fraud detection wherein you analyze transaction patterns and historical data to identify anomalies that may indicate fraudulent activities. Implementation of preventive measures to secure customer accounts and transactions can be significant and CMDM can support the provisioning of the data and the associative flagging and behavioral markers.
Naturally, enhancements to compliance and privacy measures are very topical these days and businesses want and need to implement tools and processes to ensure compliance with data protection regulations. This includes robust consent management, data encryption, and regular audits to safeguard customer information and maintain trust. Much of which is automatically provided by the Pretectum CMDM in particular.