Customer Master Data Lifecycle Management is a critical aspect of modern business operations. It involves the systematic handling of customer data from its initial collection to its eventual disposal. Effective CMDM ensures data accuracy, enhances customer relationships, and supports strategic decision-making.
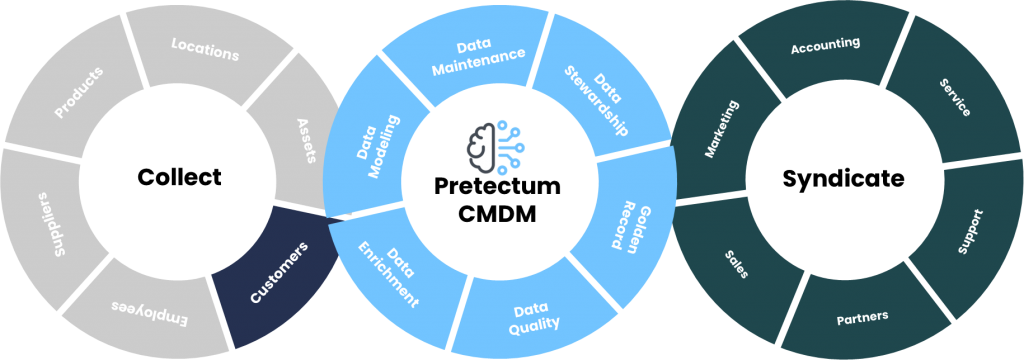
Customer master data refers to the essential information that a company maintains about customers. This data includes names, contact details, purchase history, preferences, and any other relevant information that helps in understanding and serving the customer better. Accurate and up-to-date customer data is crucial for personalized marketing, efficient service delivery, and informed business decisions.
Data Life Cycle Management is vital to ensure that customer information is correct and current, reducing errors in communication and service delivery; it enhances the ability to provide personalized experiences, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty, and helps in adhering to data protection regulations, ensuring that customer data is handled responsibly. Streamlining customer data management processes, it provides a single source of truth for customer data, reducing duplication and inconsistencies.
The are a number of stages in Customer Master Data Lifecycle Management, Data Collection, Data Storage, Maintenance, Usage, Archiving and Disposal. At each stage the Pretectum CMDM offers something of particular interest in ensuring the integrity of the end-to-end process.
Data Collection : the lifecycle begins with the collection of customer data. This can occur through various channels such as online forms, in-store interactions, and customer service calls. It is essential to collect data ethically and transparently, ensuring customers are aware of how their information will be used. Pretectum CMDM supports the data collection process by allowing you to integrate data from the data sources in situ, additionally you can bring the data via files or you can perform direct data entry via API integrations or keyboard entry.
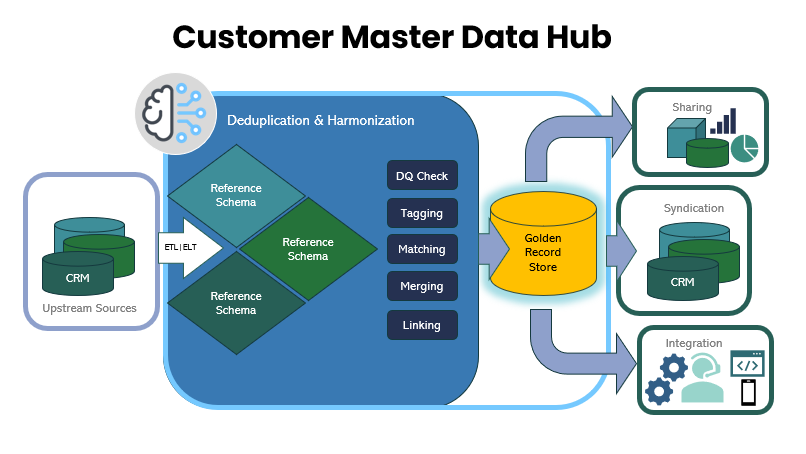
Data Storage : once collected, your customer data must be stored securely. If you’re doing this independently this involves choosing the right database systems and ensuring that data is protected against unauthorized access. Cloud-based solutions are increasingly popular due to their scalability and security features. Pretectum CMDM controls access via a number of mechanisms.
The first of these is Role Based Access Controls that allow you to define very fine grained permissions. Federated data is segregated by Business Area and allows each business unit (or system) to keep their customer data wholly independent of everyone else’s. Additional data storage aspects are the fact that Pretectum CMDM stores the customer data in an encrypted SaaS data store that can only be accessed via API or the front end of the application according to permissions. In addition, sensitive data, marked as such, is masked. Accessing the data requires specific permissions and reverification of the user’s credentials. All data events including unmasking are stored in the application history database.
Data Maintenance : no customer data repository is useful without appropriate maintenance capabilities. Maintaining data involves regular updates and validation to ensure accuracy. This includes identifying and offering the ability to correct errors, updating contact information in batches on-demand, identifying and removing duplicate entries and supporting data manipulations. Automated tools can assist in this process, reducing the manual effort required. Many of these capabilities are provided out of the box and part of the core capabilities of the Pretectum CMDM.
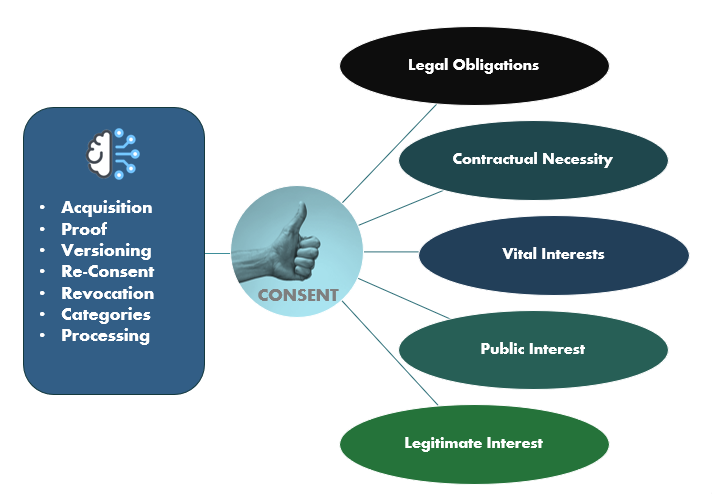
Data Usage : Is all about how customer data is used to inform various business activities, from marketing campaigns to customer service interactions. It is essential to use data responsibly, ensuring that it enhances customer experiences without infringing on privacy.
The use of customer data plays a crucial role in shaping a wide range of business activities. It informs marketing campaigns by allowing businesses to tailor their strategies to target specific demographics, preferences, and behaviors, thus increasing the effectiveness and efficiency of their promotional efforts.
By analyzing what data they have and how they might be able to leverage customer data, with a customer’s consent, businesses can identify trends and patterns that help in crafting personalized marketing messages, leading to higher engagement rates.
Customer data can be invaluable in enhancing customer service interactions; by understanding the history and preferences of their customers, businesses can provide more personalized and timely support. This might involve anticipating customer needs, offering relevant recommendations, or resolving issues more efficiently. The insights gained from customer data enable businesses to improve the overall customer experience, fostering loyalty and satisfaction.
Responsible use of customer data is of course the key. Businesses must ensure that data practices comply with privacy regulations and ethical standards. This involves obtaining explicit consent from customers for data collection, being transparent about how the data will be used, and implementing robust security measures to protect the data from breaches or misuse. By prioritizing privacy and data protection, companies build trust with their customers, ensuring that the use of data enhances rather than undermines the customer experience.
Data Archiving : becomes necessary as customers become inactive or data becomes obsolete. Stale or out of date data should be archived. Archiving involves moving data to a secure location where it can be accessed if needed but is not actively used in day-to-day operations. In fact Pretectum CMDM may hide data but it never deletes it for the purposes of maintaining an auditable history of events. This includes records that are changed, deleted or merged as a part of the deduplication process. This also means that in some particular circumstances, records and data can be reinstated should the need arise.
Data Disposal : data that is no longer needed would be disposed of securely, in other words if you will never need that data ever again, then it can be permanently deleting data to prevent unauthorized access and ensure compliance with data protection regulations. This might flow from a subject access request but more specifically it might arise when your business chooses to no longer use a particular system or technology. Unlike spreadsheets and files that might have a half life stored on network or cloud drives, or even in satellite databases, Pretectum CMDM stores all your data under your tenancy by business area in one system. When your tenancy is terminated, the data is all terminated also.
Despite its importance, CMDM is hampered by factors such as data quality, poor integration, security deficiencies and of course the ability to meet compliance obligations. When you adopt Pretectum CMDM as your preferred master data management tool for customer data, your rigor around data quality is aligned with whichever business rules you choose to establish around the management of that data.
Your integration options are only limited by the extent to which you choose to harvest and syndicate data from the Pretectum CMDM with peripheral systems like CRM, ERP and CDPs. Initially you can choose to connect via files, but you will quickly choose to securely connect and exchange data with cloud stores, databases and applications as your desire for a single customer view (SCV) grows.
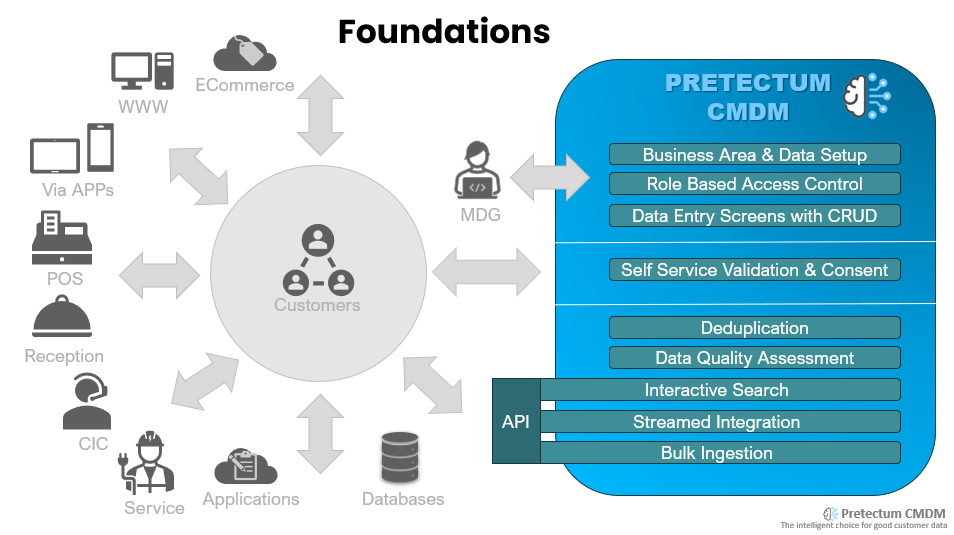
Part of your data lifecycle management process for customer master data includes how you think about data governance, the technologies that you use, your data management audit practice and the effectiveness of your employees in how they use the particular technologies.
Implement Data Governance : Establishing data governance involves creating a structured framework that outlines how data is managed, accessed, and utilized across your organization. This includes defining clear policies and procedures that dictate data handling practices. You will want to have developed a comprehensive data governance policy that covers data ownership, data stewardship, data access controls, and data lifecycle management. This will evolve according to the needs and demands in terms of maturity, of your organization and industry sector.
You will also want to have assigned specific roles and responsibilities to individuals or teams responsible for data management tasks. This includes data stewards, data custodians, and data users, each with clear accountability for maintaining data integrity and security. Finally, you will also want to have established a data governance council or committee to oversee the implementation and ongoing management of data policies and procedures. This body should include representatives from key departments such as IT, legal, compliance, and business units.
Pretectum allows you to run your customer data in a Federated Data Model, with each business unit having its own users with their own views of the data but the option to converge on a single source of truth. In addition every user is a named user and they use their own credentials and role assignments under RBAC to determine what they can see and manipulate.
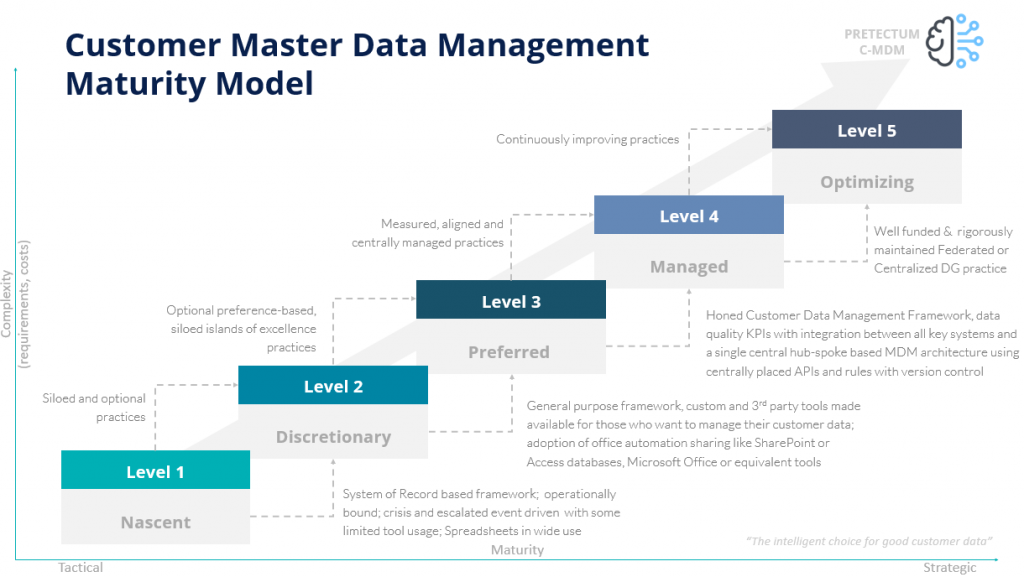
Use Advanced Technology : you’ll undoubtedly be pressured to make use of cutting-edge technologies to enhance data management capabilities. At Pretectum we’d advocate for your evaluating and implementing data management platforms that offer features such as data integration, data cleansing, and data cataloging to streamline data processes and ensure data consistency as a minimum.
Platforms may utilize artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to automate repetitive data management tasks, such as data entry, data validation, and anomaly detection, thereby reducing human error and increasing efficiency but you need to be confident that you understand how they work and switch them off if they are misaligned with your palate for risk management.
If your platform doesn’t offer data quality options out-of-the-box then investing in data quality tools that provide real-time monitoring and alerting for data discrepancies, enabling quick identification and resolution of data quality issues is pretty important in our view. Adoption of cloud-based solutions enables scalable and flexible data storage and processing, ensuring that your organization can handle growing data volumes and complex data types. Pretectum offers all of these capabilities.
Auditing Support : Conducting thorough data audits at regular intervals to assess the current state of data quality and compliance with established governance policies is most important in highly regulated industries, but it is a good practice for any business with substantial data stores. Use your audits to evaluate the effectiveness of data management practices, identify areas for improvement, and ensure that data handling procedures align with regulatory and industry standards.
Your auditors, should document their audit findings and develop action plans to address identified data quality issues, such as inconsistencies, inaccuracies, or data breaches risks. Your data teams should also involve external auditors when necessary to provide an unbiased assessment of data practices and enhance the credibility of the audit process. The Pretectum CMDM supports audit functions by way of RBAC, reporting and event logging.
Employee Training : The last point of importance is employee training and effectiveness in managing your data. you will want to develop a comprehensive training program that educates employees on the significance of data management and their role in maintaining high data quality and security standards. You should provide training sessions that cover topics such as data privacy, data protection regulations, data handling best practices, and the use of data management tools. You will also want to encourage a culture of data responsibility and accountability by promoting awareness of the potential risks and consequences of poor data management.
Continuously updated training materials that reflect changes in data policies, emerging technologies, and new regulatory requirements, ensure that employees remain informed and compliant. Ease of use, RBAC and data controls ensure that your staff are only able to perform the tasks that they are permitted to, with the greatest of ease. In application cues and clues support an accelerate learning trajectory that reinforces your employee training and data management competency objectives.
By implementing customer data management practices with Pretectum CMDM, an organization can create a robust customer data management environment that supports high-quality data, enhances operational efficiency, and ensures compliance with relevant regulations as an inherent data management practice.
Case Study: Successful Customer MDM Implementation in Retail
A leading retail company implemented a comprehensive CMDM strategy to improve their customer engagement.
They did this By integrating data from online and offline channels, creating a single customer view that allowed them to identify high value customers and ensure the greatest effectiveness in their marketing efforts.
The result was increased customer retention measured by increased average sales value. The company was also able to invest in boosted data security measures, reducing the risk of data breaches and ensuring compliance with privacy regulations and providing customers increased assurances around the management of their personal data.
Customer Master Data Lifecycle Management is a crucial aspect of modern business operations. By effectively managing customer data throughout its lifecycle, companies can enhance customer experiences, improve operational efficiency, and ensure compliance with regulations.
While challenges will likely always exist, adopting best practices and leveraging technology can help businesses overcome these obstacles and achieve success. As the market and technologies continues to evolve, good CMDM practices will remain a key factor in driving business growth and maintaining competitive advantage.
Contact us to learn more about how Pretectum CMDM can assist.


