Data-driven decision-making takes you beyond leveraging intuition and past experiences and instead makes decisions based on a thorough understanding of relevant data and information, particularly customer master data.
Such a process involves analyzing accurate and comprehensive data to guide strategic choices that align with an organization’s goals. Informed decision-making is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their operations, enhance customer experiences, and drive growth. To be most effective, you need to use appropriate, comprehensive, and quality customer data to develop your insights. This effectively serves as an evidence-based approach to guiding business choices.
This approach contrasts starkly with decisions made solely on intuition or past experiences. By leveraging customer master data, organizations can gain a clearer picture of their customer base, understand their needs and preferences, and make decisions that are more likely to yield positive outcomes.
Data-based insights and decision-making are founded upon some critical steps from data collection through analysis to evaluation, implementation, and monitoring. We will look at each of these stages and describe how the Pretectum CMDM supports these stages.
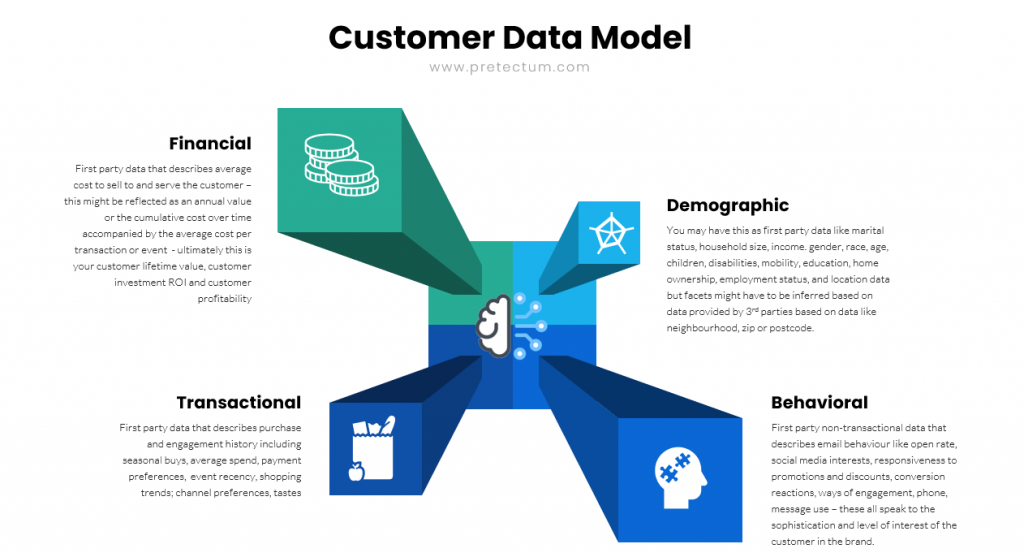
Data Collection: The foundation of informed decision-making is the collection of relevant data. For customer master data, this includes information such as demographics, purchase history, feedback, and engagement metrics.
The flexible nature of the Pretectum CMDM is such that you can define a schema or data model that is most appropriate to the needs of your business. You can consider Pretectum as a driver for your informed decision making or you can leverage the Pretectum CMDM to simply support informed decision-making. This means that you get to choose and decide just what levels of detail you want your customer master to contain.
More importantly, the data is evaluated at the time of staging, to determine fitness for purpose which is tied to the data quality definitions that you attached to the schema in question. You can use this criteria to determine which records you want o include/exclude from your analysis.
Data Analysis: Once data is collected, it needs to be analyzed to extract meaningful insights. This can involve using various analytical tools and techniques to identify trends, patterns, and correlations within the data.
Pretectum supports in-app lightweight analytics but also supports data integration through APIs to support more advanced approaches to the analysis stage. At the most basic level, the platform supports the conveyance of understanding around schema, associated metdata data tags and the relationships between datasets and schemas and reference data. The platform also informs on duplicative content and data with errors or problems.
Contextual Understanding: Understanding the context in which decisions are made is crucial. This includes recognizing the business environment, market conditions, and specific challenges or opportunities facing the organization.
This is probably the most challenging aspect of data driven analytics. Without appropriate supplementary data to support an understanding of the context not much more than the most rudimentary of analysis can be undertaken. Accordingly, one would always be encouraged to add demographic, aggregated financial, aggegrated behavioural and aggregated transaction data. Pretectum merely deals with all these additional data in the same way with no special handling beyond data typing and any attributes configured at the schema level.
Evaluation of Options: After analyzing the data, decision-makers should evaluate the potential options available to them. This involves assessing the pros and cons of each option and considering how they align with the organization’s strategic objectives.
Implementation and Monitoring: Once a decision is made, it should be implemented effectively, and its outcomes should be monitored to ensure that it delivers the expected results. Continuous feedback and data tracking can help refine future decision-making processes.
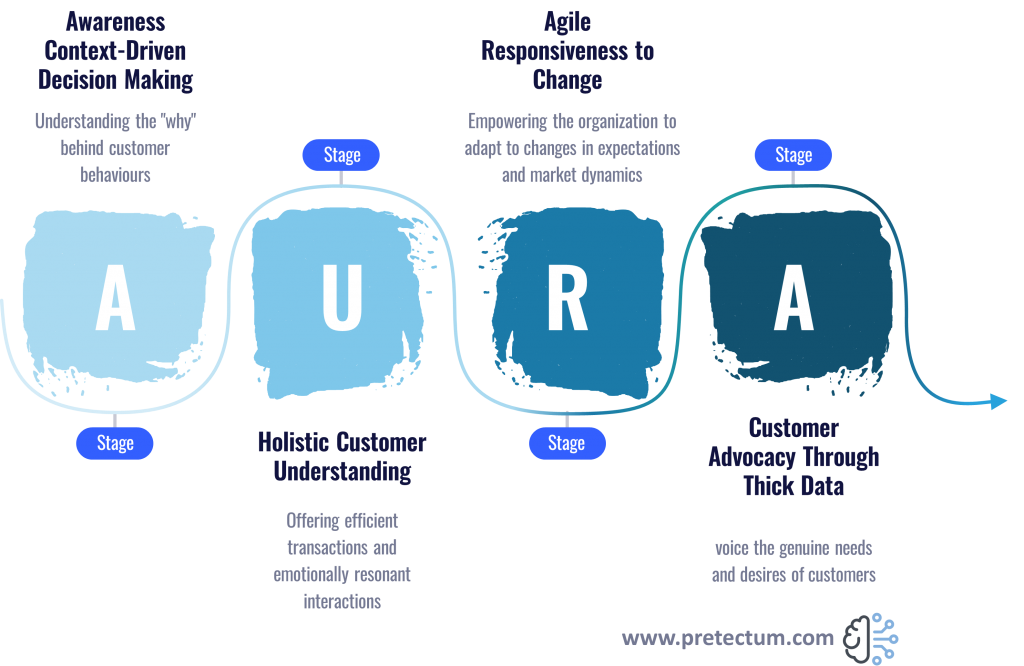
The Role of Customer Master Data in Informed Decision-Making
Customer master data plays a pivotal role in enabling informed decision-making. By consolidating and maintaining accurate customer information, businesses can create a comprehensive view of their customers, which informs various aspects of their operations. It can do this by providing ways to support personalization of customer journeys, more targeted marketing efforts, enhancing insights, operational efficiency uplifts, and risk mitigation and management
Personalization: Leveraging the 360-degree view of customers afforded by Pretectum CMDM, businesses can optimize their marketing efforts, product offerings, and customer service approaches to meet the needs and interests of the individual. This personalization can lead to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Targeted Marketing: Analysis of customer master data held within the Pretectum CMDM supports organizations in better segmentation of their customer base. By understanding different customer groups, through their data, businesses can create much more precisely targeted campaigns that resonate with the right audiences, increasing conversion and retention rates.
Enhanced Customer Insights: Only through superior customer master data in a platform like the Pretectum CMDM can organizations hope to acquire insights into customer behavior and preferences. Such information informs product development, service enhancements, and overall business strategy, ensuring that offerings align with market demand.
Operational Efficiency: By leveraging accurate customer data, organizations can streamline their processes, reduce redundancies, and minimize errors. This efficiency not only saves time and resources but also enhances the overall customer experience.
Risk Management: Informed decision-making based on reliable customer data as held within the Pretectum CMDM can help organizations identify and mitigate risks. For instance, understanding customer trends can alert businesses to potential market shifts or emerging threats especially in support of AML and KYC initiatives.
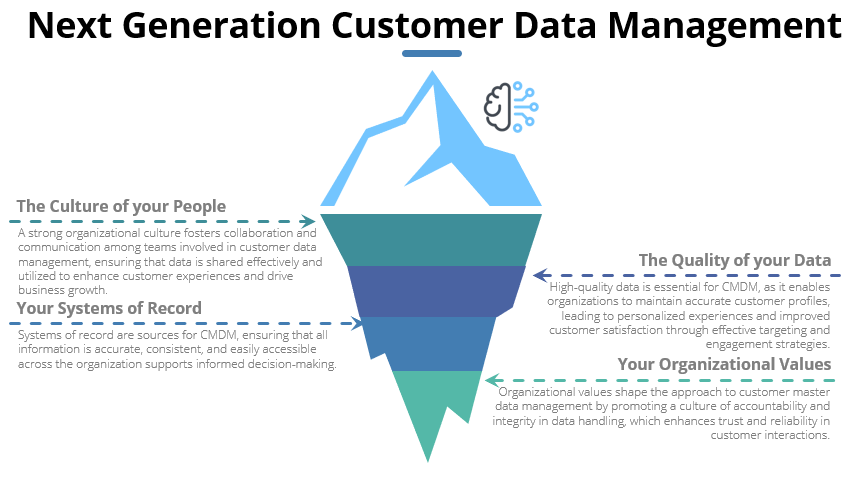
Challenges in Informed Decision-Making
While informed decision-making offers numerous benefits, organizations may face challenges in effectively utilizing customer master data. Pretectum seeks to address many of these challenges head-on.
Data Quality Issues: Poor data quality can lead to inaccurate insights, resulting in misguided decisions. Organizations must implement robust data governance practices to ensure that customer master data is accurate, complete, and up-to-date. Pretectum CMDM checks data quality as you go, providing warnings interactively and in batched data.
Data Silos: In many organizations, customer data is stored across different systems, leading to silos that hinder comprehensive analysis. Integrating data from various sources is essential for creating a unified view of customers. The federated model under which the Pretectum CMDM operates, allows users from different business units view, create or edit data according to very fine-grained RBAC permissions. Data unification under the golden nominal allows different stakeholders to converge on a single source of truth in terms of the customer profile.
Cultural Resistance: Shifting to a data-informed decision-making culture may encounter resistance from employees accustomed to relying on intuition. Organizations must foster a culture that values data and encourages collaboration across departments.The intuitive and easily navigable user interface of Pretectum CMDM combined with its provisioning in the cloud means users have access wherever they have an internet connection and credentials.
Privacy Concerns: As businesses increasingly rely on customer data, they must navigate privacy regulations and ensure that customer information is handled securely. Transparency in data usage is crucial for maintaining customer trust. Pretectum CMDM secures data at the dataset level and blocks users from access if they are not meant to have it. In addition data viewing and extraction is controlled by permissions accompanied by auditing and logging.
Informed decision-making, particularly in the context of customer master data, is essential for businesses seeking to thrive in a competitive landscape. By leveraging accurate and comprehensive customer data, organizations can make strategic choices that enhance customer experiences, drive growth, and optimize operations. The process of informed decision-making involves collecting and analyzing data, understanding the context, evaluating options, and implementing decisions effectively. While challenges such as data quality, silos, and cultural resistance may arise, the benefits of informed decision-making far outweigh the obstacles. As businesses continue to embrace data-driven strategies, the ability to make informed decisions will be a key differentiator in achieving long-term success
Contact us to learn more


