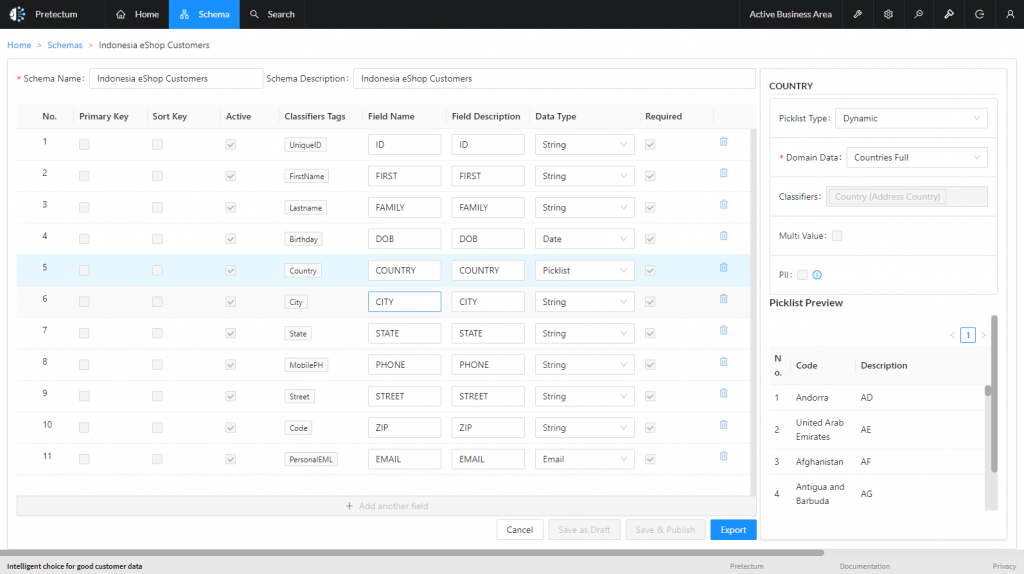
Business Area Data (BAD) or Domain Data (DD) refers to pre-defined, standardized lists of values that are critical for data validation, classification, and segmentation within the Pretectum platform. These are typically created at the time of setting up schemas for a business area.
Examples of BAD/DD:
- Geographical Identifiers: Country Codes (e.g., UK, United Kingdom), State Codes (e.g., WA, Washington), Provinces.
- Demographic Identifiers: Genders (e.g., M, Male; F, Female), Honorifics (e.g., Dr, Doctor; Mr, Mister).
- Preference Identifiers: Values representing customer preferences.
- Membership Types: Categorizations for different types of memberships.
- Typing/Classification: Any set of values useful for segmenting or classifying data within the system.
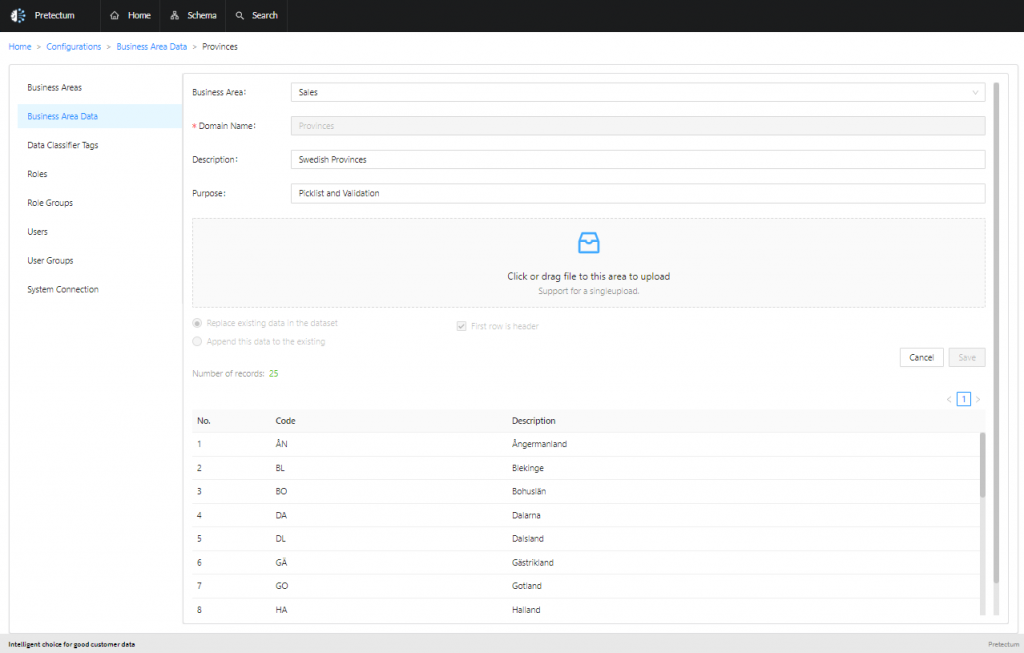
Purpose and Use of BAD/DD:
- Data Validation: BAD/DD is primarily used to validate data at the field/attribute level within a schema. When a user enters data, it can be checked against the pre-defined list of acceptable values, ensuring data quality and consistency.
- Data Picking (Picklists): BAD/DD supports the creation of picklists. When a schema field is configured to use BAD/DD, users are presented with a drop-down or selection list of valid values from that specific Business Area Data set, minimizing data entry errors.
- Data Segmentation and Classification: The “typing” aspect of BAD/DD is valuable for segmenting and classifying data. For instance, using “Membership Types” as BAD allows for easy categorization and analysis of different customer groups.
The relationship between business area data and one or more schemas is visible through the relationships view. Business area data can be business area specific or available to all business areas when stored in the DEFAULT business area.
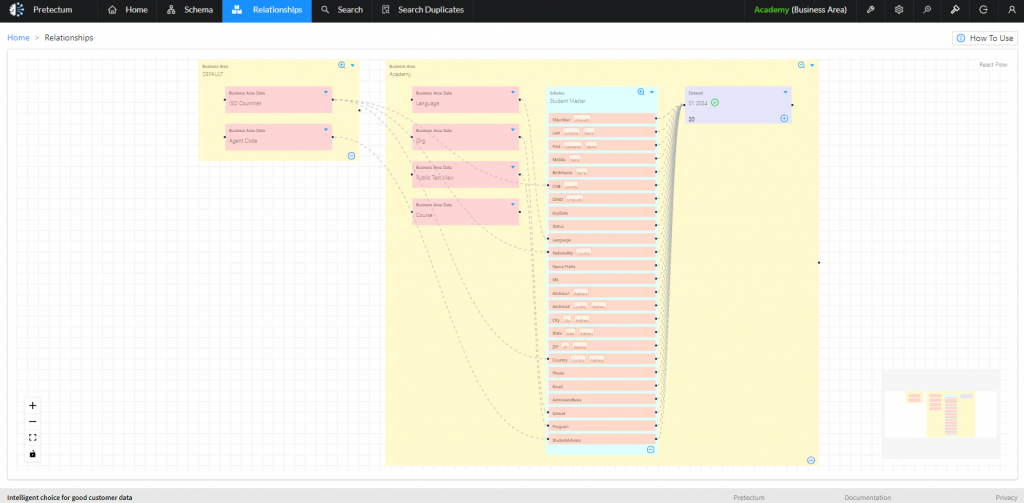
Structure of BAD/DD:
- BAD/DD is stored as pair data. This means each entry consists of two associated values, typically a short code or identifier and a longer, descriptive name.
- Examples:
WAandWashington,UKandUnited Kingdom,MandMale.
- Examples:
Management and Lifecycle of BAD/DD:
- Creation during Schema Establishment: When defining a schema, the choice of a picklist item for a specific field/attribute makes the relevant Business Area Data available as a selection option under ‘Dynamic’.
- “On-the-Fly” Picklist Creation (Disposable but Editable): Alternatively, users can create a collection of pair values “on the fly” directly within the schema setup. While these ad-hoc lists are somewhat disposable, they can still be edited from within the schema configuration.
- Centralized Maintenance: Business Area Data that is intended for broader and more permanent use needs to be maintained from a dedicated Business Area Data Configuration and Setup section. This central location supports the import of long lists of pair values, making it efficient for managing extensive domain data.
- Flexibility in Schema Lifecycle: A key advantage is that field attributes within a schema can be switched to use an existing BAD/DD at any stage in the schema’s lifecycle. This allows for evolving data validation and picklist requirements without needing to recreate the schema.